White Line Disease is extremely common in donkeys and can cause major issues if severe or left untreated.
What is White Line Disease or Seedy Toe?:
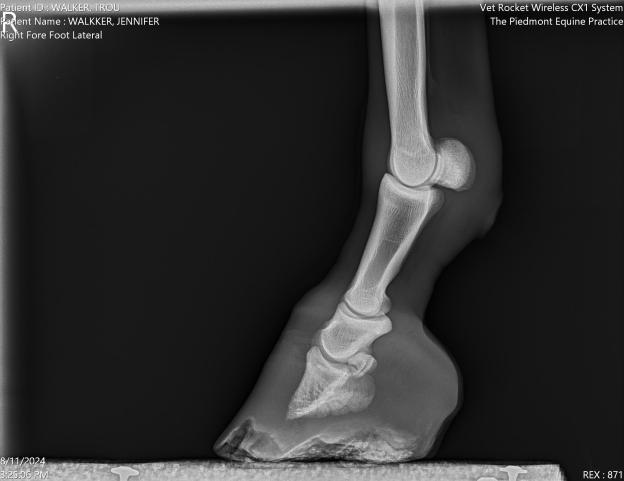
The white line is seen on the underside of the foot. It is where the unpigmented horn of the inner hoof wall joins the horn of the sole. Degeneration of the horn at the white line leads to separation of the hoof wall from the underlying structures and weakening of the hoof wall.
Risk Factors:
The reason why WLD occurs isn’t fully known, but anaerobic bacteria and fungi alongside poor foot hygiene play an important role in the development of the disease.
Some of the risk factors associated with the development of this condition are;
- 1. The presence of horn digesting microbes (Pseudoallscheria boydii, Scopulariopsis spp., Aspergillus spp, Fusobacterium necrophorum, penicillium spp.)
- 2. A wet and humid environment, poor foot hygiene,
3. Pre-existing laminitis resulting in a stretched white line
4. Hereditary factors.
Donkeys seem to be more susceptible to WLD than horses. It can affect any of the four feet and recurrence is common. Generally donkeys with WLD will not be lame, but depending on the severity of the pathology or the presence of other associated diseases, lameness could be present.
Prevention:
Maintaining good foot hygiene and regular foot care will help to prevent the occurrence of WLD. The following are best practice for prevention of this condition:
- 1. Clean the hooves daily, monitoring the integrity of the white line and the rest of hoof structures.
- 2. Change bedding frequently, avoiding humidity and accumulation of faeces and urine, especially in wet seasons.
- 3. Arrange for your farrier to check and trim the feet every six to ten weeks depending on the amount of exercise/wear, the age of the donkey and/or the presence of hoof pathology.
- 4. Avoid grease or similar products as they reduce horn oxygenation and can create an environment that encourages proliferation of horn digesting microbes.
- 5. Monitor animals with a history of WLD closely as they will be more susceptible to recurrence.
- 6. Good, clean hard standing and dry bedding are important for the health of all donkeys’ feet, but for animals with recurrent WLD it is very important.
Treatment Options:
1. Resection: Your farrier or vet will remove all the damaged horn. This procedure should not be painful but it may be necessary to remove a lot of hoof wall if the disease has progressed. In some circumstances it may be necessary to take an x-ray before removing a large amount of hoof wall to check the stability of the pedal bone.
2. Cleaning and Medicine: Once all the damaged horn has been removed, the hoof needs to be kept clean with daily hoof picking and brushing to remove as much organic matter as possible. Once the foot is clean topical disinfectants (eg povidone iodine, hydrogen peroxide or zinc sulfate) in solutions or sprays are useful to reduce microbial contamination.
3. Other Treatments: Removing all the abnormal horn, ensuring good oxygenation to the area and maintaining good foot hygiene may be enough to manage the problem. However, if the amount of wall that has been removed is substantial, your vet or farrier may decide to refill the defect with acrylic material to give more stability to the hoof capsule. In these cases it is vital that all the affected horn is removed to ensure the acrylic material bonds to healthy horn.


More Information:
https://ker.com/equinews/white-line-disease-requires-early-diagnosis-and-aggressive-treatment/