www.equisearch.com/articles/strategies-deter-horses-chewing-wood
Tag Archives: Horse Behaviors

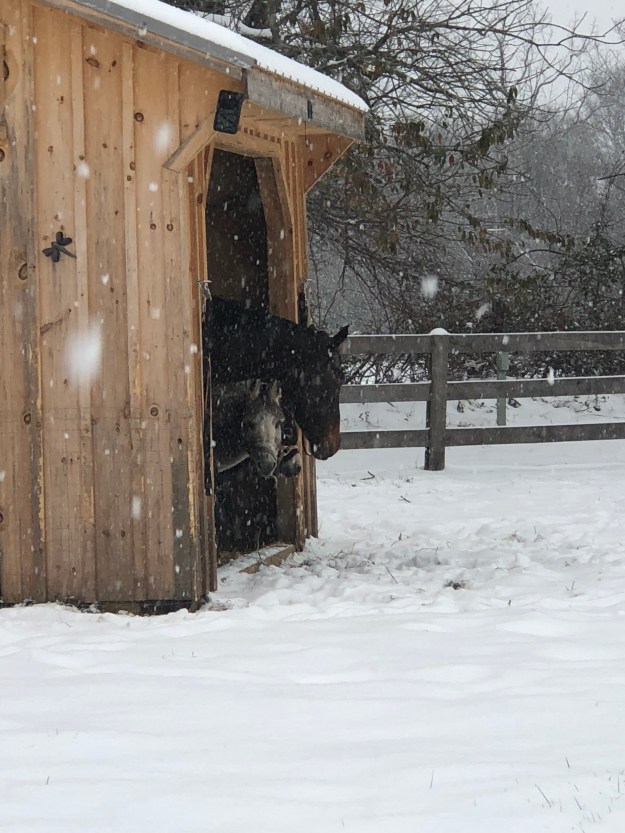
Another Day In the Snow!






Spotting Lameness: The Game Plan
Spotting Lameness: The Game Plan
— Read on horsenetwork.com/2018/10/spotting-lameness-game-plan/
Disaster Prep for Equine

You’re Always with Me
Tonight I lost my best friend, Chance. The one who whinnied the moment my car pulled up, would run away and wait for me to catch him only to turn around and run away again. He made me laugh, knew all my secrets and nuzzled me when I was sad. He taught me about unconditional love and having a positive attitude despite circumstances. He nodded when I asked if he loved me and gave kisses to get treats. He’s the 17.1 hand horse who would stand behind me and fall asleep as I did my school work and would get upset if any horse got near me but would never hurt a fly. He let children hug him and dogs run into his stall and let me dress him up with flowers. He loved rolling in the snow, laying in the sunshine, and would light up the moment he saw me. I’ll miss playing in the barn on cold nights and curling up reading in his stall when he wasn’t feeling well. I’m thankful that he waited for me to get there tonight to say goodbye so I could hold his head in my lap and talk to him while he passed. There will never be a sweeter horse with a more gentle and pure soul. Thank you, Bubba, for being with me through it all- high school, college, the break ups, the losses, the good and bad days. You gave one hell of a fight for 30+ years. Lucky and I will miss you- there will never be another you❤️ #myfavoriteredhead #chancewetake #20yearstogether #thebesthorseintheworld #myheart
Silly Donkey
The Donkey Days of Summer

The cuddliest donkey, water and a good book makes for a perfect Sunday.
It’s Raining…Lets Play!
The Welcoming Committee
Donkey See- Donkey Do

Science: When Horses Are in Trouble They Ask Humans for Help, Finds New Study
Research Fellow Monamie Ringhofer and Associate Professor Shinya Yamamoto (Kobe University Graduate School of Intercultural Studies) have proved that when horses face unsolvable problems they use visual and tactile signals to get human attention and ask for help.
The study also suggests that horses alter their communicative behavior based on humans’ knowledge of the situation. These findings were published in the online version of Animal Cognition on November 24.
Communicating with other individuals in order to get information about foraging sites and predators is a valuable survival skill. Chimpanzees, who are evolutionarily close to humans, are especially skilled at understanding others. Studies suggest that chimpanzees distinguish the attentional states of other individuals (seeing or not seeing), and they are also able to understand others’ knowledge states (knowing or not knowing).
Some domestic animals are also very good at communicating with humans—recent studies of dogs have revealed that they are excellent at understanding various human gestures and expressions. It is thought that these abilities were influenced by the domestication process.
Since they were domesticated 6000 years ago, horses have contributed to human society in various shapes and forms, from transport to companionship. Horse-riding has recently drawn attention for its positive effects on our physical and mental health. The high social cognitive skills of horses towards humans might partially explain why humans and horses have a collaborative relationship today. However, the scientific evidence for this ability is still scarce.
In this study, scientists investigated horses’ social cognitive skills with humans in a problem-solving situation where food was hidden in a place accessible only to humans. The experiment was carried out in a paddock belonging to the equestrian club at Kobe University, where eight horses from the club participated with the cooperation of their student caretakers.
For the first experiment, an assistant experimenter hid food (carrots) in a bucket that the horse could not reach. The researchers observed whether and how the horse sent signals to the caretaker when the caretaker (unaware of the situation) arrived. The horse stayed near the caretaker and looked at, touched, and pushed the caretaker. These behaviors occurred over a significantly longer period compared to cases when they carried out the experiment without hiding the food.
The results showed that when horses cannot solve problems by themselves they send signals to humans both visually (looking) and physically (touching and pushing).
Building on these results, for the second experiment they tested whether the horses’ behavior changed based on the caretakers’ knowledge of the hidden food. If the caretaker hadn’t watched the food being hidden, the horses gave more signals, demonstrating that horses can change their behavior in response to the knowledge levels of humans.
These two experiments revealed some behaviors used by horses to communicate demands to humans. They also suggest that horses possess high cognitive skills that enable them to flexibly alter their behavior towards humans according to humans’ knowledge state. This high social cognitive ability may have been acquired during the domestication process.
In order to identify the characteristic that enables horses to form close bonds with humans, in future research the team aims to compare communication between horses, as well as looking more closely at the social cognitive ability of horses in their communication with humans.
By deepening our understanding of the cognitive abilities held by species who have close relationships with humans, and making comparisons with the cognitive abilities of species such as primates who are evolutionarily close to humans, we can investigate the development of unique communication traits in domesticated animals.
This is connected to the influence of domestication on the cognitive ability of animals, and can potentially provide valuable information for realizing stronger bonds between humans and animals.

Figure 1. Horse making demands: The horse a) lightly pushes and b) looks at the caretaker standing outside the paddock. Food is hidden inside one of the two silver buckets behind them. When horses cannot obtain this food by themselves, they give humans visual and tactile signals.

Photo provided by Monamie Ringhofer.
Figure 2. Horse with caretaker at the equestrian club

Keeping Your Horse Safe on the 4th of July
When I think of the Fourth of July, I think of a fun time with my family and friends. Typically, I am not thinking of the potentially hazardous effects the fireworks may have on my animals…. Why would you? However, the truth is, the boom of the fireworks and the bright and sudden flashes can not only cause our horses severe anxiety but may also lead to injury.
Have you ever been in the dark and someone shines a flashlight in your eyes? What happens? You see spots. You are momentarily unable to see. Your balance gets thrown off and you can’t tell what is right in front of you. Well, imagine a horse. He is in a dark paddock and suddenly flashes of light momentarily blind him and add in the boom…recipe for disaster. Not only can he barely see but he spooks from the noise. The results could be anxiety to tripping and breaking a leg. That being said, I have included some useful information below for ways to safeguard your horse this July 4th.
Fireworks and Horses: Preparing for the Big Boom | TheHorse.com

EPM Tilter. What Do The Numbers Mean?
During my horse’s recent Lymphingitis flare-up, the vet advised that we run labs to test for Lyme and EPM due to his presenting symptoms (hind weakness, twisting his back leg at the walk/walking sideways I refer to it as- “Chance’s swagger”). As I noted previously, Chance’s Lyme test revealed that he was at the beginning stages of an acute infection…yay for the labs at Cornell University for their amazing ability to give you more than a positive or negative!
A little history before getting to the EPM Tilter results.
About 2ish years ago, Chance was diagnosed with EPM (and one of the reasons opossums and I are not friends since they host the disease as do a few other culprits). Chance immediately began EPM treatment- he received Protazil in his feed for one month. After hours of research I chose Protazil, although extremely expensive (if you order from http://www.drfosterandsmith.com they sometimes have promotions where you receive store credit for every $100.00 you spend…they did when I ordered and I got a “free” dog bed that my dogs adore), due to the decreased likelihood of Chance experiencing a “Treatment Crisis” (worsening of symptoms) and the ease of administration (other brands require the drug being administered 1 hour before eating or an hour after and so on). Typically, EPM treatment is done for 30 days and, depending on the residual symptoms, some may require subsequent treatments. While Chance’s symptoms improved, I wanted to ensure that we annihilated the disease and did another round of treatment but this time with Marquis. At the end of two months, Chance’s ataxia was gone!
Fast forward to September 2016…Chance, just having a Lymphingitis flare-up, has been tested for Lyme and EPM. Lyme came back positive. And….so did the EPM test..well, kind of. Wonderful. (See why I loathe opossums?)
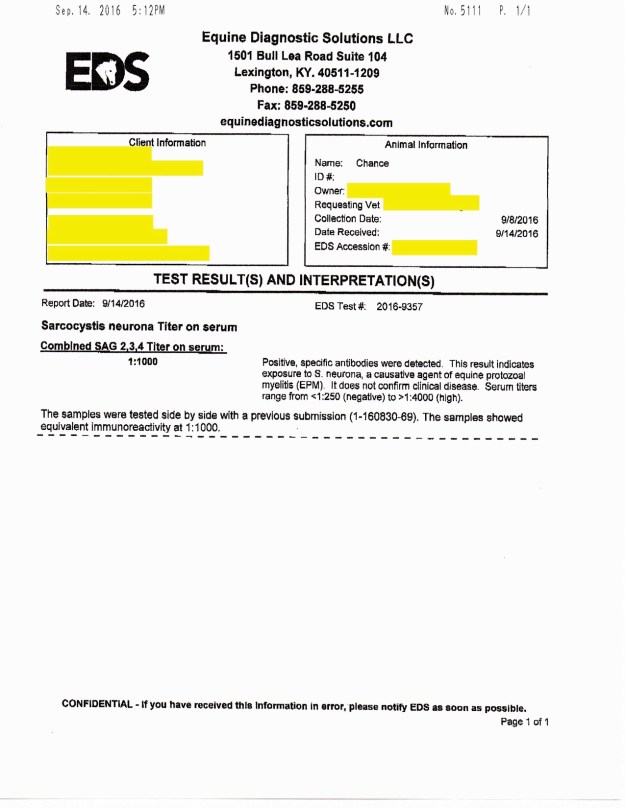
Chance’s EPM test #2 on 8/30/16 (the 1st one was 2ish years ago) showed the following:
“Combined SAG 2,3,4 Tilter on serum= 1:2000”
So, what does this mean?
The test revealed that Chance had “positive, specific antibodies” detected in the blood work. This means that he had EXPOSURE to S. Neurona, a causative agent of EPM. Serum tilters range from <1:250 (negative) to >1:4000 (high positive). S. Neurona (SarcoFluor) is one of two protozoa found in EPM infected horses, the other protazoa is N. Hughesil (NeoFluor). S. Neurona is most frequently seen, whereas N. Hughesil is not as common.
The vet ran another EPM test to confirm the findings in the 8/30/16 test. The results showed that Chance had “Combined SAG 2,3,4 Tilter on serum= 1:1000. Again, Chance showed EPM protozoa in the positive-ish range.
I initially had not seen the results but was told by the vet that he was EPM negative. So when I asked for the test results to be emailed to me and saw the numbers I sort of freaked out…I emailed the vet to ask for clarification. She explained,
“The EPM test shows that he was exposed to the organism in the first test we did which is why we did a follow-up test. Since his exposure level dropped from 1:2000 to 1:1000 this shows that he does not have the disease. There is no good one time test for EPM once they are exposed which is why we had to do the repeat to compare the two.”
While this explanation offered me comfort, I was confused…why does he have any protozoa in his blood if he doesn’t have EPM?
I spoke to another vet and she explained it in a bit more detail…I am hoping I am summarizing what she said correctly..
When a horse tests positive for EPM they either have an active disease or they may not. However, when the test does from 1:2000 down to 1:1000 this typically means that the horse’s immune system is working correctly to fight the disease off- active or not. EPM testing typically provides you with a % of the chance your horse has an active EPM infection, or at least if you send it to Cornell University. For instance, lets say a horse gets the results back and it shows that they are “positive” or have been exposed to S. Neurona (one of the two EPM protozoa)…their results are 1:647. This means that, after doing a bunch of adding and multiplying that this vet kindly did for me, the horse has a 60-70% chance of having ACTIVE EPM. Meaning, he most likely would be symptomatic (ie: behavioral changes, ataxia, weight loss, difficulty eating, changes in soundness, and a bunch of other neurological symptoms).
My hunch is that Chance’s immune system was boosted because I started him on Transfer Factor (amazing stuff… more information can be found in some of my older posts) again as soon as his results came back positive for Lyme.
Here are the 3 EPM tilters that were run on Chance (oldest to most recent) along with his Lyme test results:



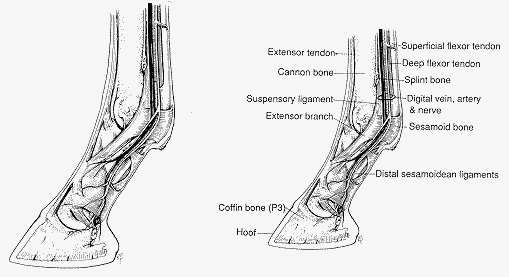
I have a limp!
Resources on how to diagnose, treat, prevent, and handle lameness in horses
Your Horse Has a Swollen Leg – Why and What To Do | EquiMed – Horse Health Matters
Fetlock Lameness – It’s importance… | The Horse Magazine – Australia’s Leading Equestrian Magazine
Causes of Equine Lameness | EquiMed – Horse Health Matters
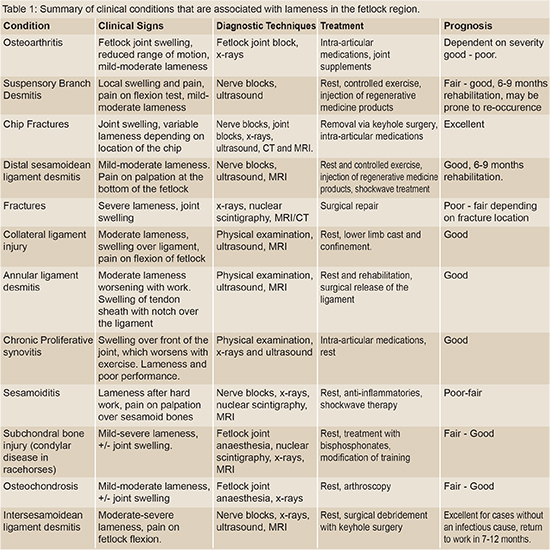
Common Causes of Lameness in the Fetlock

Where’s Lucky?








