During my horse’s recent Lymphingitis flare-up, the vet advised that we run labs to test for Lyme and EPM due to his presenting symptoms (hind weakness, twisting his back leg at the walk/walking sideways I refer to it as- “Chance’s swagger”). As I noted previously, Chance’s Lyme test revealed that he was at the beginning stages of an acute infection…yay for the labs at Cornell University for their amazing ability to give you more than a positive or negative!
A little history before getting to the EPM Tilter results.
About 2ish years ago, Chance was diagnosed with EPM (and one of the reasons opossums and I are not friends since they host the disease as do a few other culprits). Chance immediately began EPM treatment- he received Protazil in his feed for one month. After hours of research I chose Protazil, although extremely expensive (if you order from http://www.drfosterandsmith.com they sometimes have promotions where you receive store credit for every $100.00 you spend…they did when I ordered and I got a “free” dog bed that my dogs adore), due to the decreased likelihood of Chance experiencing a “Treatment Crisis” (worsening of symptoms) and the ease of administration (other brands require the drug being administered 1 hour before eating or an hour after and so on). Typically, EPM treatment is done for 30 days and, depending on the residual symptoms, some may require subsequent treatments. While Chance’s symptoms improved, I wanted to ensure that we annihilated the disease and did another round of treatment but this time with Marquis. At the end of two months, Chance’s ataxia was gone!
Fast forward to September 2016…Chance, just having a Lymphingitis flare-up, has been tested for Lyme and EPM. Lyme came back positive. And….so did the EPM test..well, kind of. Wonderful. (See why I loathe opossums?)
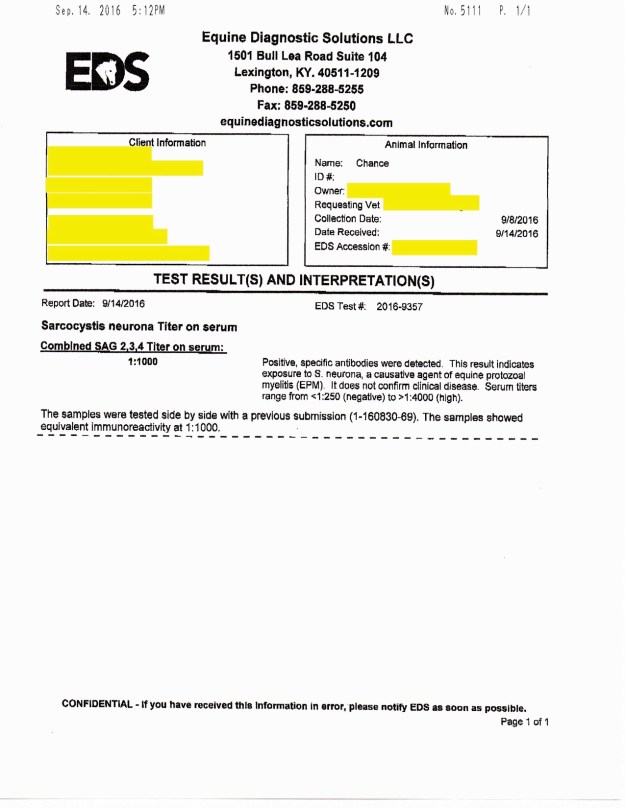
Chance’s EPM test #2 on 8/30/16 (the 1st one was 2ish years ago) showed the following:
“Combined SAG 2,3,4 Tilter on serum= 1:2000”
So, what does this mean?
The test revealed that Chance had “positive, specific antibodies” detected in the blood work. This means that he had EXPOSURE to S. Neurona, a causative agent of EPM. Serum tilters range from <1:250 (negative) to >1:4000 (high positive). S. Neurona (SarcoFluor) is one of two protozoa found in EPM infected horses, the other protazoa is N. Hughesil (NeoFluor). S. Neurona is most frequently seen, whereas N. Hughesil is not as common.
The vet ran another EPM test to confirm the findings in the 8/30/16 test. The results showed that Chance had “Combined SAG 2,3,4 Tilter on serum= 1:1000. Again, Chance showed EPM protozoa in the positive-ish range.
I initially had not seen the results but was told by the vet that he was EPM negative. So when I asked for the test results to be emailed to me and saw the numbers I sort of freaked out…I emailed the vet to ask for clarification. She explained,
“The EPM test shows that he was exposed to the organism in the first test we did which is why we did a follow-up test. Since his exposure level dropped from 1:2000 to 1:1000 this shows that he does not have the disease. There is no good one time test for EPM once they are exposed which is why we had to do the repeat to compare the two.”
While this explanation offered me comfort, I was confused…why does he have any protozoa in his blood if he doesn’t have EPM?
I spoke to another vet and she explained it in a bit more detail…I am hoping I am summarizing what she said correctly..
When a horse tests positive for EPM they either have an active disease or they may not. However, when the test does from 1:2000 down to 1:1000 this typically means that the horse’s immune system is working correctly to fight the disease off- active or not. EPM testing typically provides you with a % of the chance your horse has an active EPM infection, or at least if you send it to Cornell University. For instance, lets say a horse gets the results back and it shows that they are “positive” or have been exposed to S. Neurona (one of the two EPM protozoa)…their results are 1:647. This means that, after doing a bunch of adding and multiplying that this vet kindly did for me, the horse has a 60-70% chance of having ACTIVE EPM. Meaning, he most likely would be symptomatic (ie: behavioral changes, ataxia, weight loss, difficulty eating, changes in soundness, and a bunch of other neurological symptoms).
My hunch is that Chance’s immune system was boosted because I started him on Transfer Factor (amazing stuff… more information can be found in some of my older posts) again as soon as his results came back positive for Lyme.
Here are the 3 EPM tilters that were run on Chance (oldest to most recent) along with his Lyme test results: